Shusaku Uchida

氏名Name
Shusaku Uchida
所属・職名Affiliation, Title, etc.
Department of Integrative Stress Science
Medical Research Laboratory, Institute of Integrated Research
Institute of Science Tokyo
Professor
研究室HPWebsite
一言メッセージShort Message
本プロジェクトでの研究概要Outline of the research in this project
慢性的なストレスや抑うつ状態はアルツハイマー病などの認知症の発症リスクを増大させることが指摘されています。逆境や困難な状況にも関わらず精神的健康を維持・回復できる能力、すなわちレジリエンスを高めることは、神経精神疾患の予防・回復を促す可能性があります。これまでの研究成果から、ストレスレジリエンスとは個人的特性に加えて集団による社会的な防御/回復因子と回復に向けた力動的過程と記述できます。つまり、多層的な因子によって新たな均衡状態を創り出すリザバー機構の発動がレジリエンスを高めて疾患の予防や早期回復につながる可能性があります。そこで本研究では、ストレスレジリエンスを誘導する脳内メカニズムを同定して神経疾患からの早期回復を実現するためのリザバー機構増強技術を開発します。本研究により、レジリエンスのメカニズムを解明して科学的エビデンスに基づいた神経疾患に資する脳リザバー機構増強法の基盤技術を確立します。
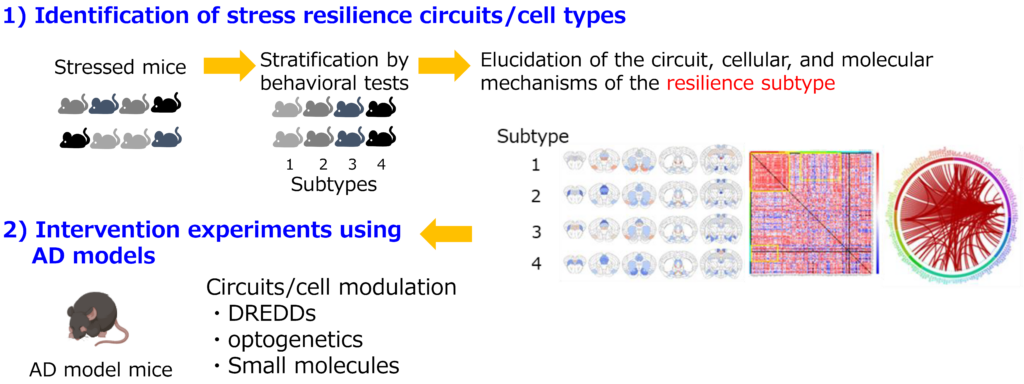
Chronic stress and depression are known to increase the risk of developing dementia such as Alzheimer's disease. Enhancing resilience, the ability to maintain and recover mental health despite adversity and risk, may promote the prevention and recovery of neuropsychiatric disorders. Based on previous researches, stress resilience can be described as a dynamic process of recovery, as well as individual characteristics and social protective/recovery factors. In other words, the activation of a reservoir mechanism that generates a new equilibrium state through multi-scale factors may lead to the prevention of disease onset and early recovery. In this project, we will identify the brain mechanisms that induce stress resilience and develop technologies to enhance the reservoir mechanism in order to achieve early recovery from neurological disorders. Through this research, we will elucidate the mechanisms of resilience and establish the basic technology for enhancing the brain reservoir mechanism for neurological disorders based on scientific evidence.

これまで主な研究内容Outline of main research so far
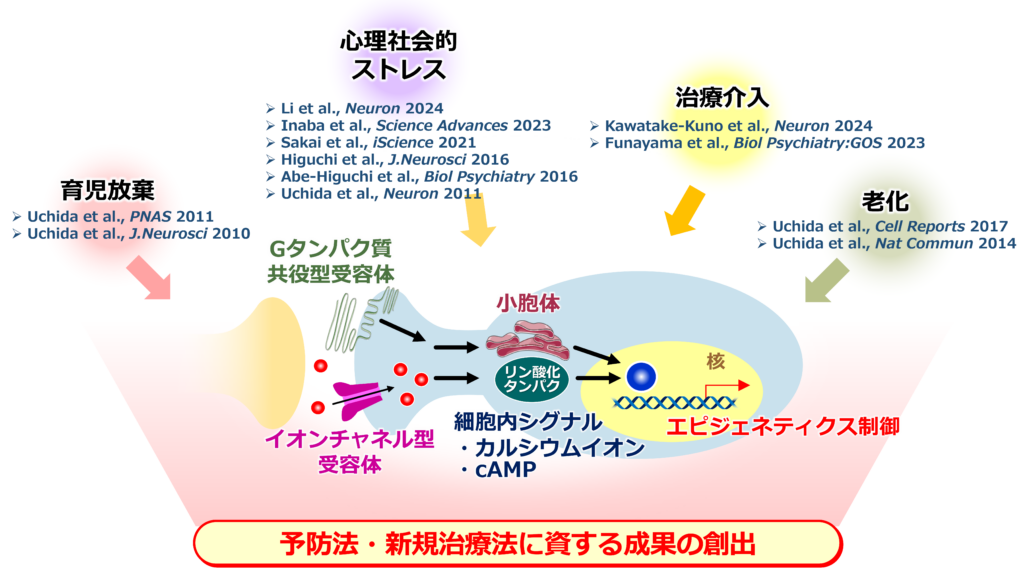
“Molecular and neural basis of stress resilience in the brain”
Excessive stress is known to increase the risk of developing depression and anxiety disorders. However, not everyone who is exposed to stress develops mental disorders. Resilience, which is a protective or buffering factor against stressors, is thought to have two aspects: the ability to maintain a healthy mental state even when exposed to stressors, and the ability to recover from difficult situations. Although “Gene X Environmental factor interaction” is believed to be involved in the mechanism that gives rise to individual differences in sensitivity to stress and the manifestation of symptoms, the actual nature of this has been unclear. We have been conducting research to clarify the causal relationship, not just the phenomenology, by analyzing the effects of external environmental factors such as maternal separation, psychosocial stress, aging, and therapeutic intervention on the brain at multi-scale levels, including molecular, cellular, circuit, and behavioral levels, using stress resilience model mice and stress sensitivity model mice. So far, we have discovered novel molecular pathways and neural circuits related to stress resilience and behavioral change. We have also discovered drug seeds such as small molecule compounds from these results.
主な経歴・受賞歴等Career, Awards, etc.
Career
- 2005
- Graduate School of Agricultural Chemistry, Tokyo University of Agriculture
- 2005-2011
- Assistant Professor, Yamaguchi University Graduate School of Medicine
- 2011-2013
- Postdoc, Department of Genetics, Rutgers University
- 2013-2018
- Associate Professor, Yamaguchi University Hospital
- 2018-2024
- Program-Specific Associate Professor, Medical Innovation Center, Graduate School of Medicine, Kyoto University
- 2024-2025
- Associate Professor, Nagoya City University Graduate School of Medicine
- 2025-Present
- Professor, Department of Integrative Stress Science, Medical Research Laboratory, Institute of Integrated Research, Institute of Science Tokyo
主要業績Major Publications
A. Kawatake-Kuno, H. Li, H. Inaba, M. Hikosaka, E. Ishimori, T. Ueki, Y. Garkun, H. Morishita, S. Narumiya, N. Osishi, G. Ohtsuki, T. Murai, S. Uchida, Sustained antidepressant effects of ketamine metabolite involve GABAergic inhibition-mediated molecular dynamics in aPVT glutamatergic neurons, Neuron, 2024 112(8):1265-1285.
H. Li, A. Kawatake-Kuno, H. Inaba, Y. Miyake, Y. Itoh, T. Ueki, N. Oishi, T. Murai, T. Suzuki, S. Uchida, Discrete prefrontal neuronal circuits determine repeated stress-induced behavioral phenotypes in male mice, Neuron, 2024, 112, 786-804.
H. Inaba, H. Li, A. Kawatake-Kuno, K. Dewa, J. Nagai, N. Oishi, T. Murai, S. Uchida, GPCR-mediated calcium and cAMP signaling determines psychosocial stress susceptibility and resiliency, Science Advances, 2023, 9, eade5397.
Y. Sakai, H. Li, H. Inaba, Y. Funayama, E. Ishimori, A. Kawatake-Kuno, H. Yamagata, T. Seki, T. Hobara, S. Nakagawa, Y. Watanabe, S. Tomita, T. Murai, S. Uchida, Gene-environment interactions mediate stress susceptibility and resilience through the CaMKIIβ/TARPγ-8/AMPAR pathway, iScience, 2021, 24, 102504.
S. Uchida, BJ. Teubner, C. Hevi, K. Hara, A. Kobayashi, RM. Dave, T. Shintaku, P. Jaikhan, H. Yamagata, T. Suzuki, Y. Watanabe, SS. Zakharenko, GP. Shumyatsky, CRTC1 Nuclear Translocation Following Learning Modulates Memory Strength via Exchange of Chromatin Remodeling Complexes on the Fgf1 Gene, Cell Reports, 2017, 18, 352-366.
G. Martel, S. Uchida, C. Hevi, I. Chévere-Torres, I. Fuentes, YJ. Park, H. Hafeez, H. Yamagata, Y. Watanabe, GP. Shumyatsky, Genetic demonstration of a role for stathmin in adult hippocampal neurogenesis, spinogenesis, and NMDA receptor-dependent memory, Journal of Neuroscience, 2016, 36, 1185-1202.
F. Higuchi, S. Uchida, H. Yamagata, N. Abe-Higuchi, T. Hobara, K. Hara, A. Kobayashi, T. Shintaku, Y. Itoh, T. Suzuki, Y. Watanabe, Hippocampal MicroRNA-124 Enhances Chronic Stress Resilience in Mice, Journal of Neuroscience, 2016, 36, 7253-7267.
S. Uchida, G. Martel, A. Pavlowsky, S. Takizawa, C. Hevi, Y. Watanabe, ER. Kandel, JM. Alarcon, GP. Shumyatsky, Learning-induced and stathmin-dependent changes in microtubule stability are critical for memory and disrupted in ageing, Nature Communications, 2014, 5, 4389.
S. Uchida, K. Hara, A. Kobayashi, M. Fujimoto, K. Otsuki, H. Yamagata, T. Hobara, N. Abe, F. Higuchi, T. Shibata, S. Hasegawa, S. Kida, A. Nakai, Y. Watanabe, Impaired hippocampal spinogenesis and neurogenesis and altered affective behavior in mice lacking heat shock factor 1, PNAS, 2011, 108, 1681-1686.
S. Uchida, K. Hara, A. Kobayashi, K. Otsuki, H. Yamagata, T. Hobara, T. Suzuki, N. Miyata, Y. Watanabe, Epigenetic status of Gdnf in the ventral striatum determines susceptibility and adaptation to daily stressful events, Neuron, 2011, 69, 359-372.



